library("gamlss2")
## packages, code, and data
library("distributions3")
data("cars", package = "datasets")
## fit heteroscedastic normal GAMLSS model
## stopping distance (ft) explained by speed (mph)
m <- gamlss2(dist ~ s(speed) | s(speed), data = cars, family = NO)GAMLSS-RS iteration 1: Global Deviance = 405.737 eps = 0.128969
GAMLSS-RS iteration 2: Global Deviance = 405.7368 eps = 0.000000 ## obtain predicted distributions for three levels of speed
d <- prodist(m, newdata = data.frame(speed = c(10, 20, 30)))
print(d) 1 2
"GDF NO(mu = 23.06, sigma = 10.06)" "GDF NO(mu = 58.98, sigma = 18.53)"
3
"GDF NO(mu = 96.14, sigma = 34.12)" ## obtain quantiles (works the same for any distribution object 'd' !)
quantile(d, 0.5) 1 2 3
23.05774 58.98303 96.14450 quantile(d, c(0.05, 0.5, 0.95), elementwise = FALSE) q_0.05 q_0.5 q_0.95
1 6.509283 23.05774 39.60620
2 28.505214 58.98303 89.46086
3 40.028584 96.14450 152.26042quantile(d, c(0.05, 0.5, 0.95), elementwise = TRUE) 1 2 3
6.509283 58.983035 152.260421 ## visualization
plot(dist ~ speed, data = cars)
nd <- data.frame(speed = 0:240/4)
nd$dist <- prodist(m, newdata = nd)
nd$fit <- quantile(nd$dist, c(0.05, 0.5, 0.95))
matplot(nd$speed, nd$fit, type = "l", lty = 1, col = "slategray", add = TRUE)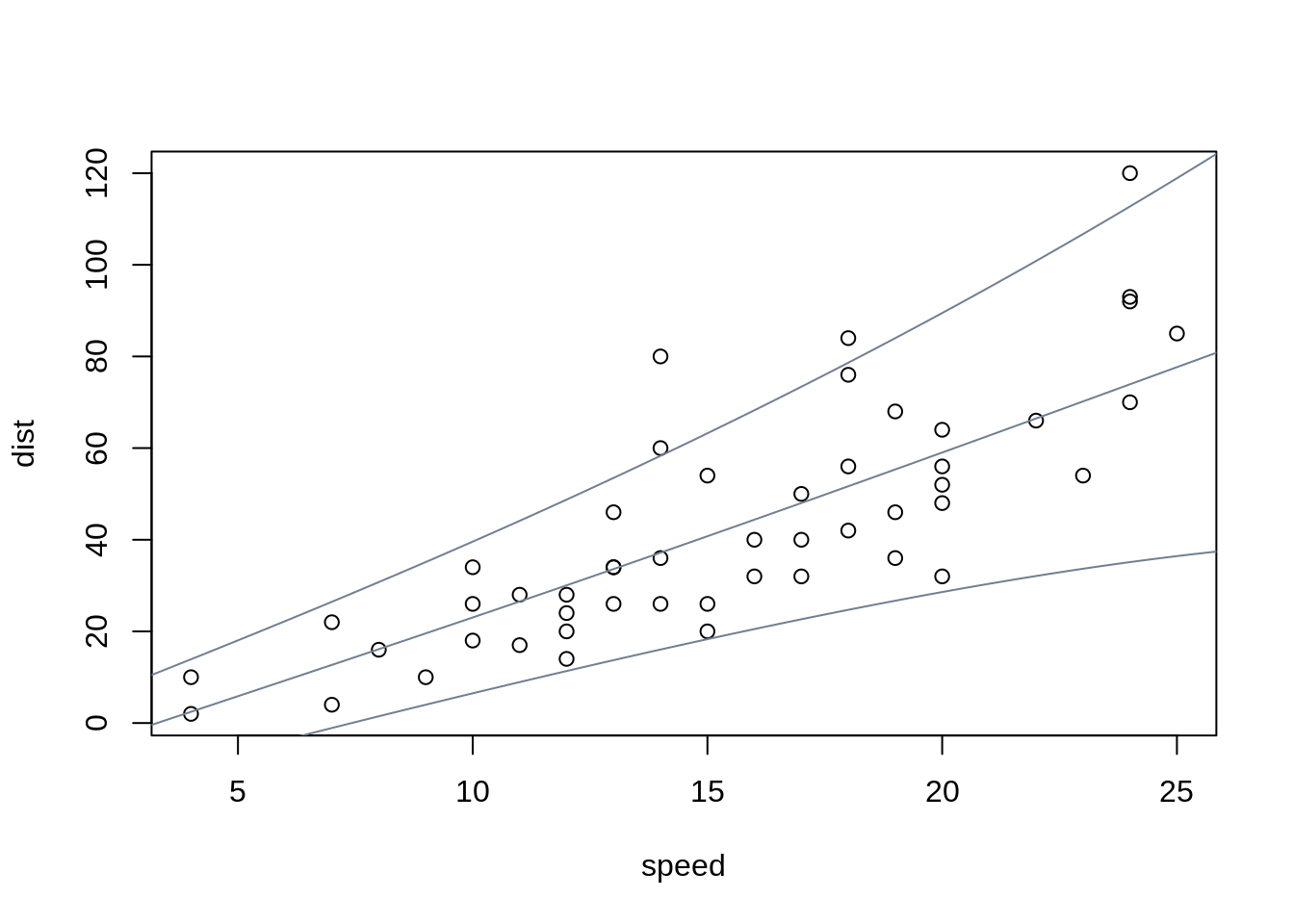
## moments
mean(d) 1 2 3
23.05774 58.98303 96.14450 variance(d) 1 2 3
101.2187 343.3312 1163.9053 ## simulate random numbers
random(d, 5) r_1 r_2 r_3 r_4 r_5
1 28.16977 26.73513 30.07320 8.469816 27.73499
2 57.47088 61.59268 73.31481 60.529487 67.36702
3 94.68376 62.76397 157.74447 72.796019 95.92022## density and distribution
pdf(d, 50 * -2:2) d_-100 d_-50 d_0 d_50 d_100
1 1.291599e-34 1.405182e-13 0.0028687701 0.001099050 7.901284e-15
2 2.223063e-18 6.622130e-10 0.0001357331 0.019143272 1.857756e-03
3 7.765882e-10 1.211145e-06 0.0002204765 0.004684784 1.161925e-02cdf(d, 50 * -2:2) p_-100 p_-50 p_0 p_50 p_100
1 1.055415e-34 1.911829e-13 0.0109571049 0.99629637 1.0000000
2 4.738088e-18 2.030474e-09 0.0007281644 0.31390760 0.9865732
3 4.479859e-09 9.188654e-06 0.0024149871 0.08809582 0.5449892## Poisson example
data("FIFA2018", package = "distributions3")
m2 <- gamlss2(goals ~ s(difference), data = FIFA2018, family = PO)GAMLSS-RS iteration 1: Global Deviance = 355.3922 eps = 0.045332
GAMLSS-RS iteration 2: Global Deviance = 355.3922 eps = 0.000000 d2 <- prodist(m2, newdata = data.frame(difference = 0))
print(d2) 1
"GDF PO(mu = 1.237)" quantile(d2, c(0.05, 0.5, 0.95))[1] 0 1 3## note that log_pdf() can replicate logLik() value
sum(log_pdf(prodist(m2), FIFA2018$goals))[1] -177.6961logLik(m2)'log Lik.' -177.6961 (df=2.005144)