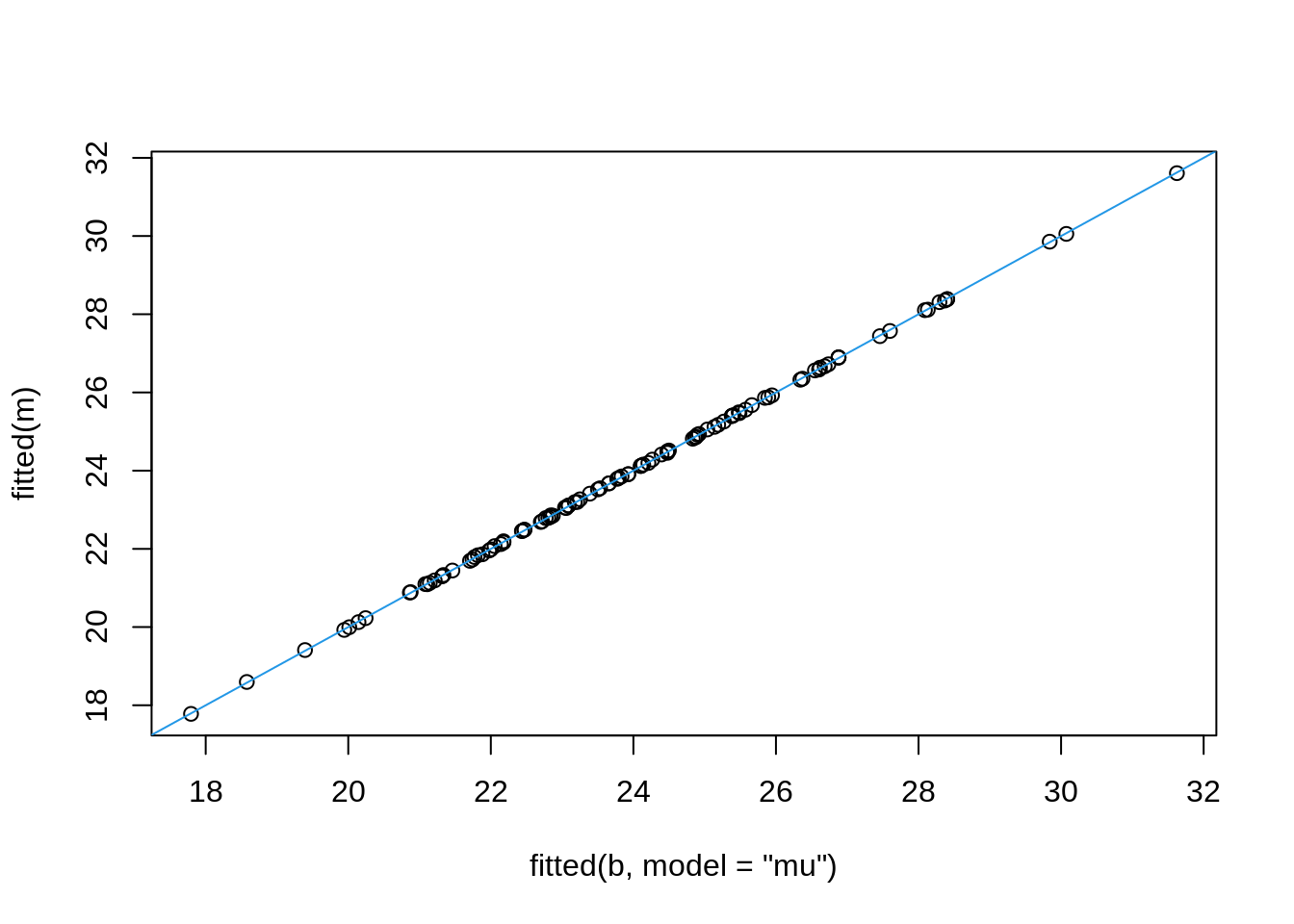
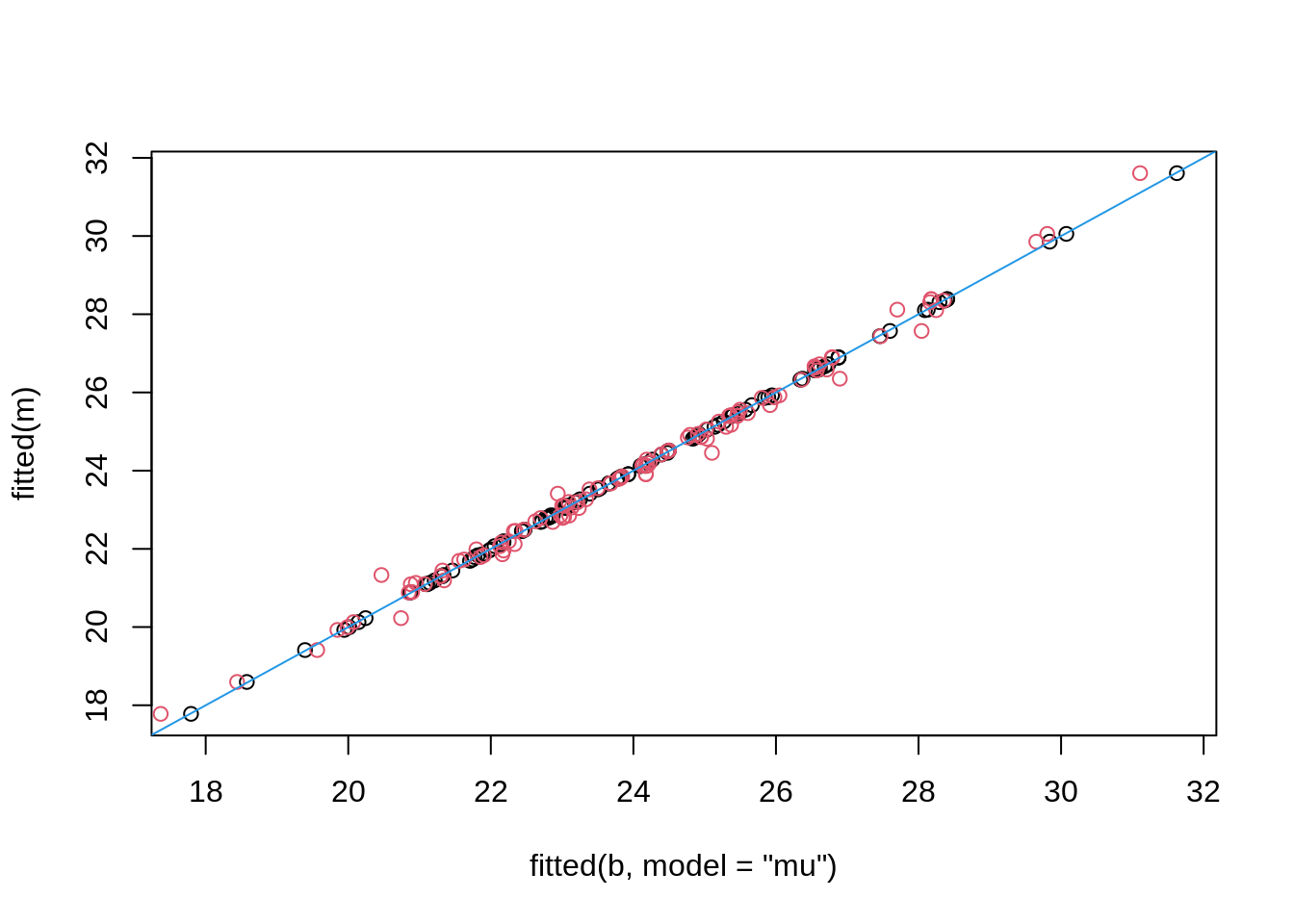
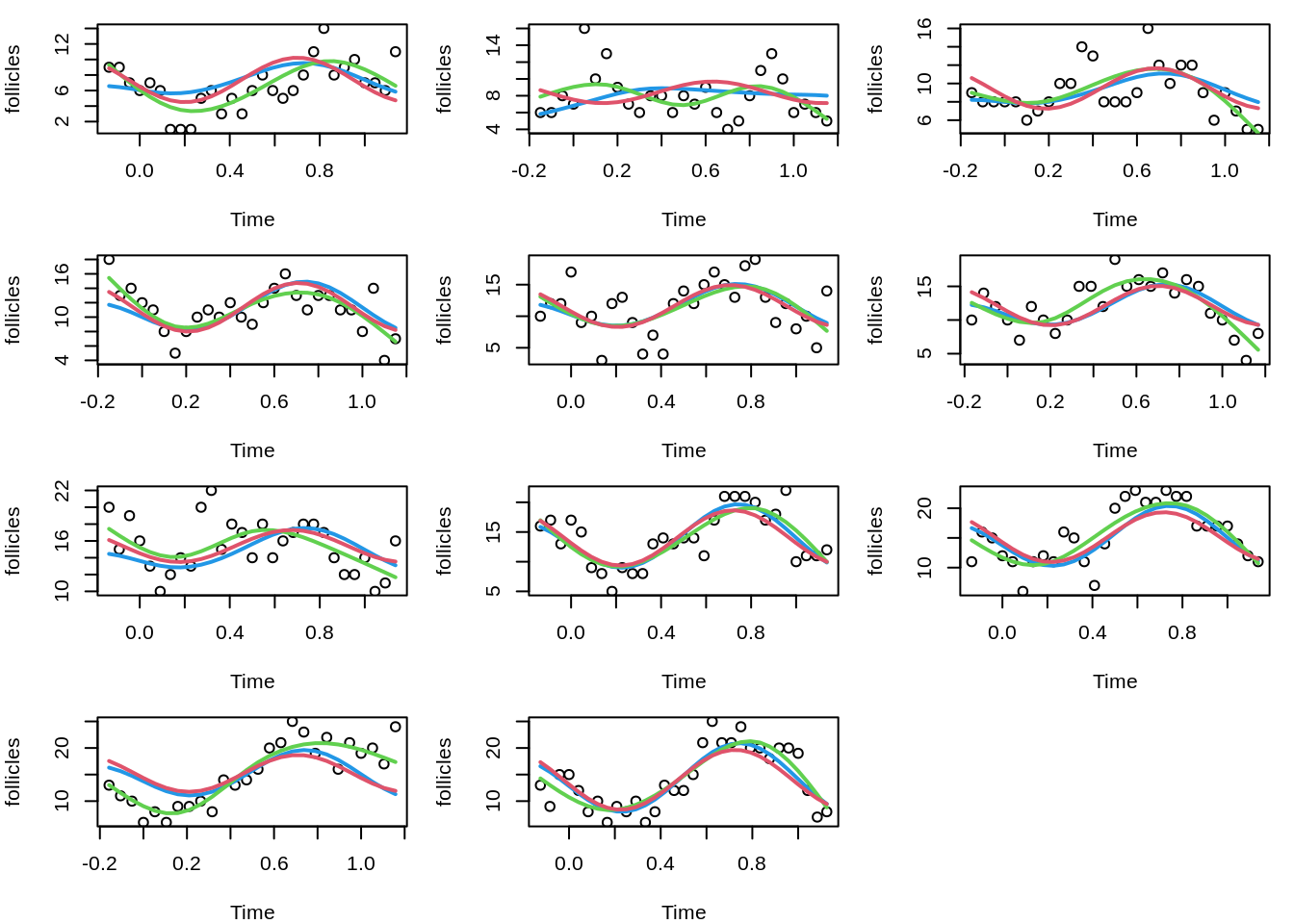
Linear mixed-effects model fit by maximum likelihood
Data: structure(list(age11 = c(-3, -1, 1, 3, -3, -1, 1, 3, -3, -1, 1, 3, -3, -1, 1, 3, -3, -1, 1, 3, -3, -1, 1, 3, -3, -1, 1, 3, -3, -1, 1, 3, -3, -1, 1, 3, -3, -1, 1, 3, -3, -1, 1, 3, -3, -1, 1, 3, -3, -1, 1, 3, -3, -1, 1, 3, -3, -1, 1, 3, -3, -1, 1, 3, -3, -1, 1, 3, -3, -1, 1, 3, -3, -1, 1, 3, -3, -1, 1, 3, -3, -1, 1, 3, -3, -1, 1, 3, -3, -1, 1, 3, -3, -1, 1, 3, -3, -1, 1, 3, -3, -1, 1, 3, -3, -1, 1, 3), Subject = structure(c(15L, 15L, 15L, 15L, 3L, 3L, 3L, 3L, 7L, 7L, 7L, 7L, 14L, 14L, 14L, 14L, 2L, 2L, 2L, 2L, 13L, 13L, 13L, 13L, 5L, 5L, 5L, 5L, 6L, 6L, 6L, 6L, 11L, 11L, 11L, 11L, 16L, 16L, 16L, 16L, 4L, 4L, 4L, 4L, 8L, 8L, 8L, 8L, 9L, 9L, 9L, 9L, 10L, 10L, 10L, 10L, 12L, 12L, 12L, 12L, 1L, 1L, 1L, 1L, 20L, 20L, 20L, 20L, 23L, 23L, 23L, 23L, 25L, 25L, 25L, 25L, 26L, 26L, 26L, 26L, 21L, 21L, 21L, 21L, 19L, 19L, 19L, 19L, 22L, 22L, 22L, 22L, 24L, 24L, 24L, 24L, 18L, 18L, 18L, 18L, 17L, 17L, 17L, 17L, 27L, 27L, 27L, 27L), levels = c("M16", "M05", "M02", "M11", "M07", "M08", "M03", "M12", "M13", "M14", "M09", "M15", "M06", "M04", "M01", "M10", "F10", "F09", "F06", "F01", "F05", "F07", "F02", "F08", "F03", "F04", "F11"), class = c("ordered", "factor")), response_z = c(3.95740740740771, 1.63703703703704, 4.31666666666667, 4.9962962962963, -0.542592592592602, -0.862962962962968, -1.68333333333333, 0.496296296296297, 0.957407407407398, -0.862962962962968, -0.683333333333334, 1.4962962962963, 3.4574074074074, 4.13703703703703, 1.81666666666666, 0.996296296296297, -2.0425925925926, 0.137037037037032, -2.18333333333333, -0.00370370370369955, 2.4574074074074, 2.13703703703704, 2.31666666666666, 2.4962962962963, -0.0425925925926016, -1.36296296296297, -0.183333333333334, 0.496296296296297, 1.9574074074074, -1.86296296296297, -0.183333333333334, -0.5037037037037, 0.957407407407398, -2.86296296296297, 6.31666666666666, -0.00370370370369955, 5.45740740740739, 4.63703703703703, 6.31666666666666, 5.49629629629629, 0.957407407407398, -0.362962962962968, -1.18333333333333, -1.0037037037037, -0.542592592592602, 0.137037037037032, -0.683333333333334, 1.9962962962963, -5.0425925925926, 1.13703703703703, 1.31666666666667, 3.4962962962963, 0.457407407407402, 2.13703703703704, 0.81666666666667, -0.00370370370369955, 0.957407407407402, 1.13703703703703, 1.31666666666667, 3.9962962962963, -0.0425925925926016, -1.86296296296297, -1.18333333333333, -1.0037037037037, -1.0425925925926, -3.36296296296297, -3.18333333333333, -3.0037037037037, -1.0425925925926, -1.86296296296297, -0.683333333333334, -0.5037037037037, -1.5425925925926, 0.637037037037032, -0.183333333333334, -0.00370370370369955, 1.4574074074074, 1.13703703703703, 0.316666666666666, 0.496296296296297, -0.542592592592602, -0.362962962962968, -2.18333333333333, -2.5037037037037, -2.0425925925926, -2.36296296296297, -3.68333333333334, -3.5037037037037, -0.542592592592602, -0.862962962962968, -1.68333333333333, -1.0037037037037, 0.957407407407398, -0.362962962962968, -1.18333333333333, -2.0037037037037, -2.04259259259261, -2.36296296296297, -2.68333333333333, -4.5037037037037, -5.5425925925926, -4.36296296296297, -5.68333333333334, -6.5037037037037, 2.4574074074074, 1.63703703703704, 3.31666666666666, 1.9962962962963), weights_w = c(0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369, 0.116596837376369)), terms = ~age11 + Subject, row.names = c(NA, 108L), class = "data.frame")
AIC BIC logLik
449.2116 462.6223 -219.6058
Random effects:
Formula: ~age11 | Subject
Structure: General positive-definite, Log-Cholesky parametrization
StdDev Corr
(Intercept) 2.0906352 (Intr)
age11 0.2149235 0.521
Residual 3.8365552
Variance function:
Structure: fixed weights
Formula: ~weights_w
Fixed effects: response_z ~ 1
Value Std.Error DF t-value p-value
(Intercept) 6.064444e-16 0.4048917 81 1.497794e-15 1
Standardized Within-Group Residuals:
Min Q1 Med Q3 Max
-3.305976369 -0.487428882 0.007598099 0.482237876 3.922787577
Number of Observations: 108
Number of Groups: 27